Keyword: Toxic Cyanobacteria
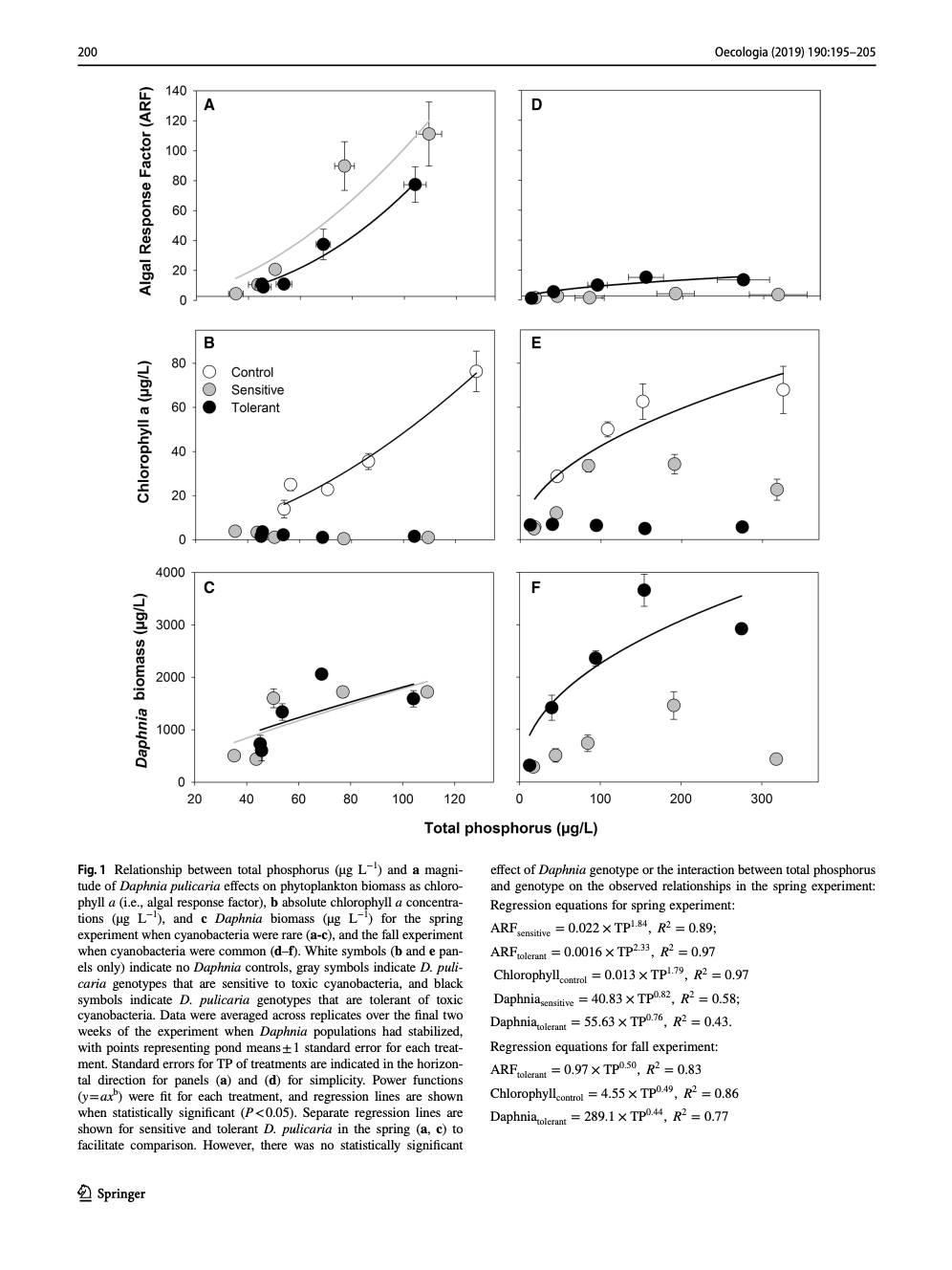
Chislock, M. F., O. Sarnelle, L. M. Jernigan, V. R. Anderson, A. Abebe, and A. E. Wilson. 2019. Consumer adaptation mediates top-down regulation across a productivity gradient. Oecologia 190:195-205.
Abstract
Humans have artificially enhanced the productivity of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems on a global scale by increasing nutrient loading. While the consequences of eutrophication are well known (e.g., harmful algal blooms and toxic cyanobacteria), most studies tend to examine short-term responses relative to the time scales of heritable adaptive change. Thus, the potential role of adaptation by organisms in stabilizing the response of ecological systems to such perturbations is largely unknown. We tested the hypothesis that adaptation by a generalist consumer (Daphnia pulicaria) to toxic prey (cyanobacteria) mediates the response of plankton communities to nutrient enrichment. Overall, the strength of Daphnia’s top–down effect on primary producer biomass increased with productivity. However, these effects were contingent on prey traits (e.g., rare vs. common toxic cyanobacteria) and consumer genotype (i.e., tolerant vs sensitive to toxic cyanobacteria). Tolerant Daphnia strongly suppressed toxic cyanobacteria in nutrient-rich ponds, but sensitive Daphnia did not. In contrast, both tolerant and sensitive Daphnia genotypes had comparable effects on producer biomass when toxic cyanobacteria were absent. Our results demonstrate that organismal adaptation is critical for understanding and predicting ecosystem-level consequences of anthropogenic environmental perturbations.
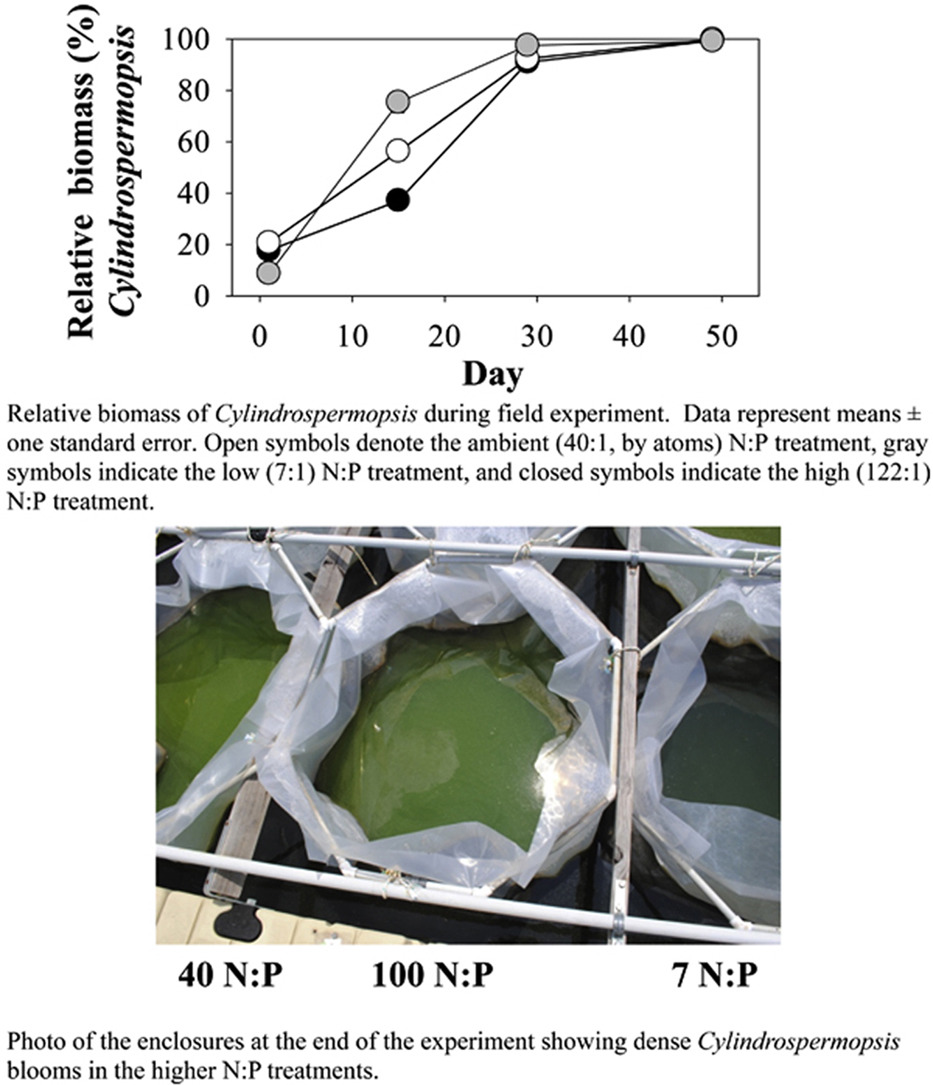
Chislock, M. F., K. L. Sharp, and A. E. Wilson. 2014. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii dominates under very low and high nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios. Water Research 49:207-214.
Abstract
In freshwater ecosystems, a variety of factors mediate phytoplankton community structure, including herbivore community structure, light availability, temperature, mixing, and absolute and relative nutrient concentrations (total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP)). Ecological stoichiometry examines how the nutrient content of organisms and their environment may mediate population-, community-, and ecosystem-level processes. The manipulation of N:P ratios is a widely regarded tool for managing phytoplankton species composition given that nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria should dominate algal communities under relatively low N:P (<64:1, by atoms) given their ability to convert dissolved dinitrogen gas into organic nitrogen. However, due to the physiological expense of nitrogen fixation, diazotrophs should be outcompeted by non-nitrogen fixing phytoplankton under higher N:P when other environmental factors are similar. We tested this hypothesis in a field experiment using 2500-L limnocorrals installed in a eutrophic lake (ambient N:P ∼40:1 (by atoms); TN ∼1360 μg L−1; TP ∼75 μg L−1). At the start of the experiment, we randomly assigned limnocorrals among the ambient (40:1) and low (7:1) or high (122:1) N:P treatments (n = 4 replicates/treatment), which were established by adding P or N at the start of the experiment, respectively. The phytoplankton community in the enclosures at the start of the experiment was diverse (i.e., 18 phytoplankton genera) and dominated by chlorophytes (including Coelastrum and Scenedesmus (30% and 13% of total biomass, respectively)) and cyanobacteria (including Anabaena and Cylindrospermopsis (23% and 17% of total biomass, respectively)). In contrast to predictions based on ecological stoichiometry, the phytoplankton community in all N:P treatments increased in abundance and was almost entirely composed of the nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, by the conclusion of the study. Moreover, concentrations of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin, saxitoxin, were enhanced under the two highest N:P conditions. The ability of C. raciborskii to dominate phytoplankton communities under such extreme N:P shows that short-term management of nutrient stoichiometry through fertilization is not likely to be effective for controlling blooms of this noxious cyanobacterium and may help to explain the rapid expansion of this invasive species to temperate latitudes.
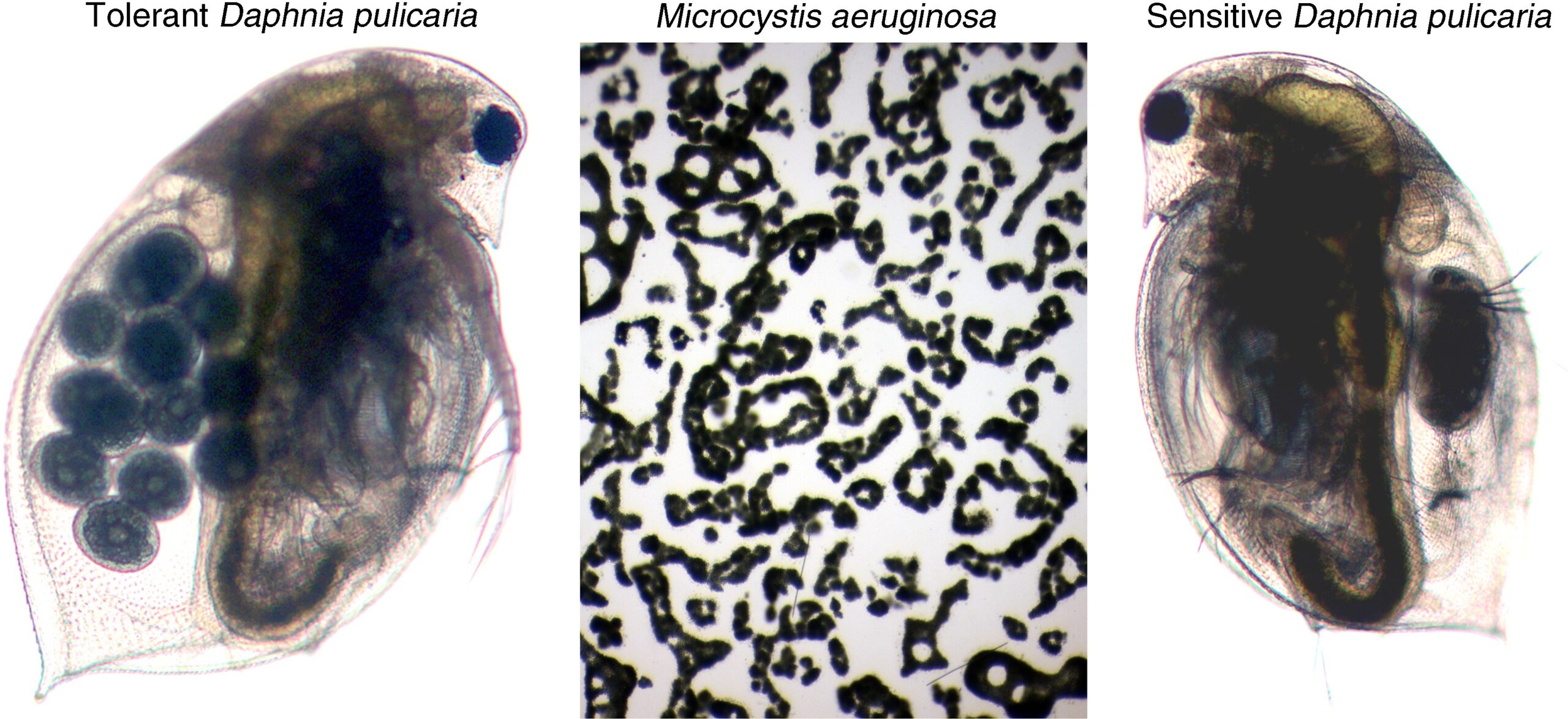
Chislock, M. F., O. Sarnelle, B. K. Olsen, E. Doster, and A. E. Wilson. 2013. Large effects of consumer offense on ecosystem structure and function. Ecology 94(11):2375-2380.
Abstract
Study of the role of within-species adaptation in ecological dynamics has focused largely on prey adaptations that reduce consumption risk (prey defense). Few, if any, studies have examined how consumer adaptations to overcome prey defenses (consumer offense) affect ecosystem structure and function. We manipulated two sets of genotypes of a planktonic herbivore (Daphnia pulicaria) in a highly productive ecosystem with abundant toxic prey (cyanobacteria). The two sets of consumer genotypes varied widely in their tolerance of toxic cyanobacteria in the diet (i.e., sensitive vs. tolerant). We found a large effect of tolerant D. pulicaria on phytoplankton biomass and gross primary productivity but no effect of sensitive genotypes, this result stemming from genotype-specific differences in population growth in the presence of toxic prey. The former effect was as large as effects seen in previous Daphnia manipulations at similar productivity levels. Thus, we demonstrated that the effect of consumer genotypes with contrasting offensive adaptations was as large as the effect of consumer presence/absence.
Berry, J. P., E. Lee, K. Walton, A. E. Wilson, and F. Bernal-Brooks. 2011. Microcystin production by a persistent cyanobacterial bloom in Lago de Patzcuaro (Michiacan, Mexico) and apparent bioaccumulation of the toxin in small commercial catches of fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 30(7):1621-1628.
Abstract
Lago de Patzcuaro is a historically important freshwater fishery in Mexico. The lake is presently characterized by a persistent bloom of cyanobacteria, specifically dominated by recognized producers of toxic microcystins (MCYSTs). We evaluated MCYSTs in sestonic and dissolved fractions of the water column, as well as representative fish species (silversides, Chirostoma spp.; Goodea sp.; and carp, Cyprinus carpio) obtained from local markets and small commercial catches during the bloom. Samples were evaluated primarily by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and secondarily by protein phosphatase (PPase) inhibition assay and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Sestonic MCYST concentration (0.02-0.36 µg/L) generally correlated inversely with distance from the bloom, supporting the bloom as the source of the toxin. Several MCYST variants, including MC-LR, -LA and -LY, as well as didemethyl variants, were identified by LC-MS/MS analysis. All three species of fish bioaccumulated MCYSTs in relevant tissues, and toxin content correlated with trophic level, with highest and lowest levels measured in phytoplanktivorous and zooplanktivorous representatives, respectively. Detection of MCYST in silversides and Goodea sp. is particularly relevant because both are consumed in their entirety, including viscera (e.g., liver) known to primarily accumulate MCYST. These results indicate that Lago de Patzcuaro is indeed characterized by a toxigenic bloom, and that commercially important fish species from the lake accumulate toxic MCYST in tissues relevant to human consumption. As such, this system may represent an ideal model of the trophic transfer of MCYSTs and its relevance to human and environmental health.